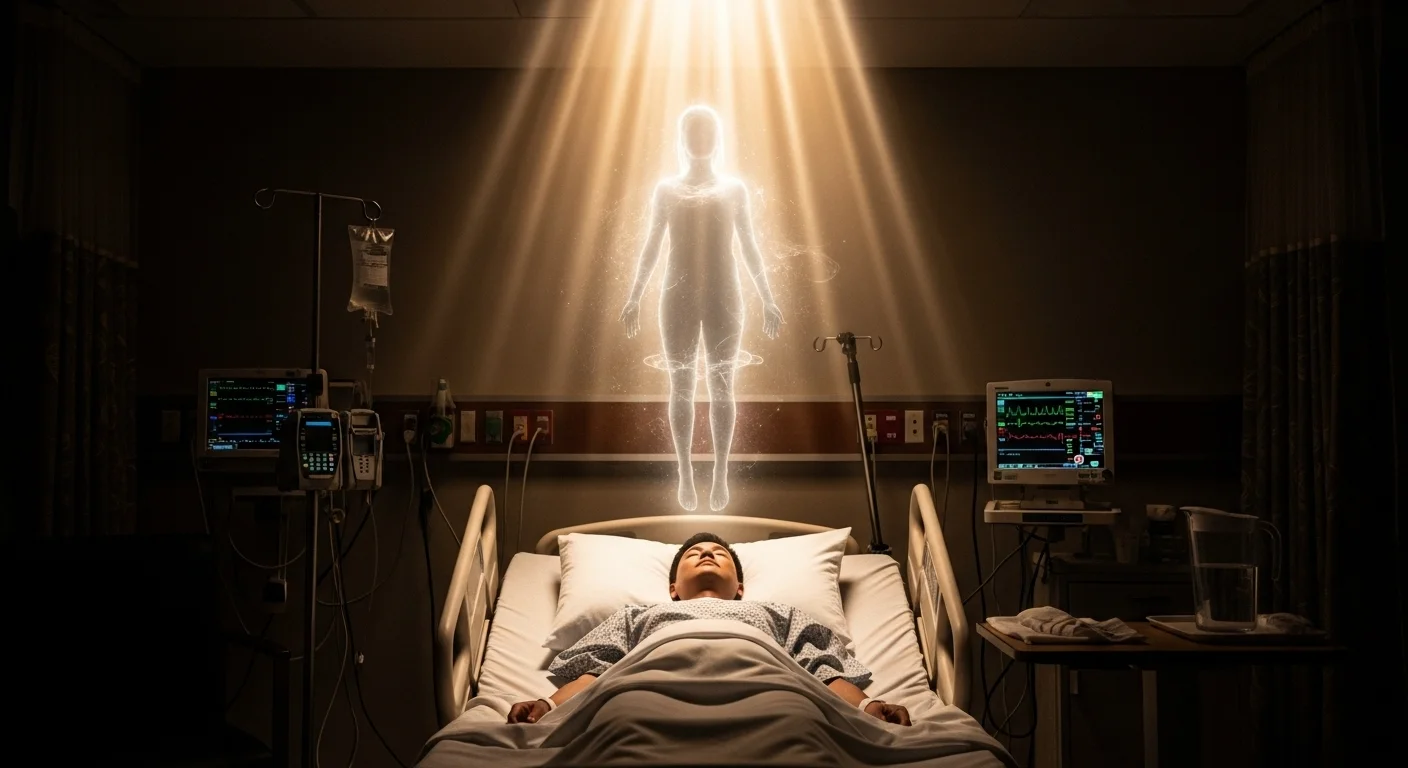
A near-death experience is a distinct psychological event that occurs when a person is close to death. This often happens during medical emergencies like cardiac arrest or severe physical trauma. The individual retains a sense of lucidity and awareness despite being clinically unconscious. Researchers define it as a specific state of consciousness rather than a dream or a hallucination. The event is universal and appears across different cultures and age groups without significant variation in the core details.
Clinical definitions rely on a set of recurrent characteristics reported by survivors. The most common element is the sensation of separating from the physical body. Individuals often describe observing their surroundings from a different vantage point. Other frequent features include moving through a dark tunnel or encountering a brilliant light. Some people also report meeting deceased family members or reviewing key moments from their lives. These specific components help experts identify and classify the phenomenon accurately.
Medical professionals use standardized scales to evaluate these reports objectively. They assess the intensity and content of the narrative to confirm the diagnosis. A genuine near-death experience typically results in long-term changes in personality and outlook. Survivors often demonstrate a significant decrease in the fear of death after the event. They also tend to show increased empathy and a renewed purpose in life. This transformative effect distinguishes the phenomenon from transient mental states caused by medication or injury.

Description of the Out-of-Body Sensation
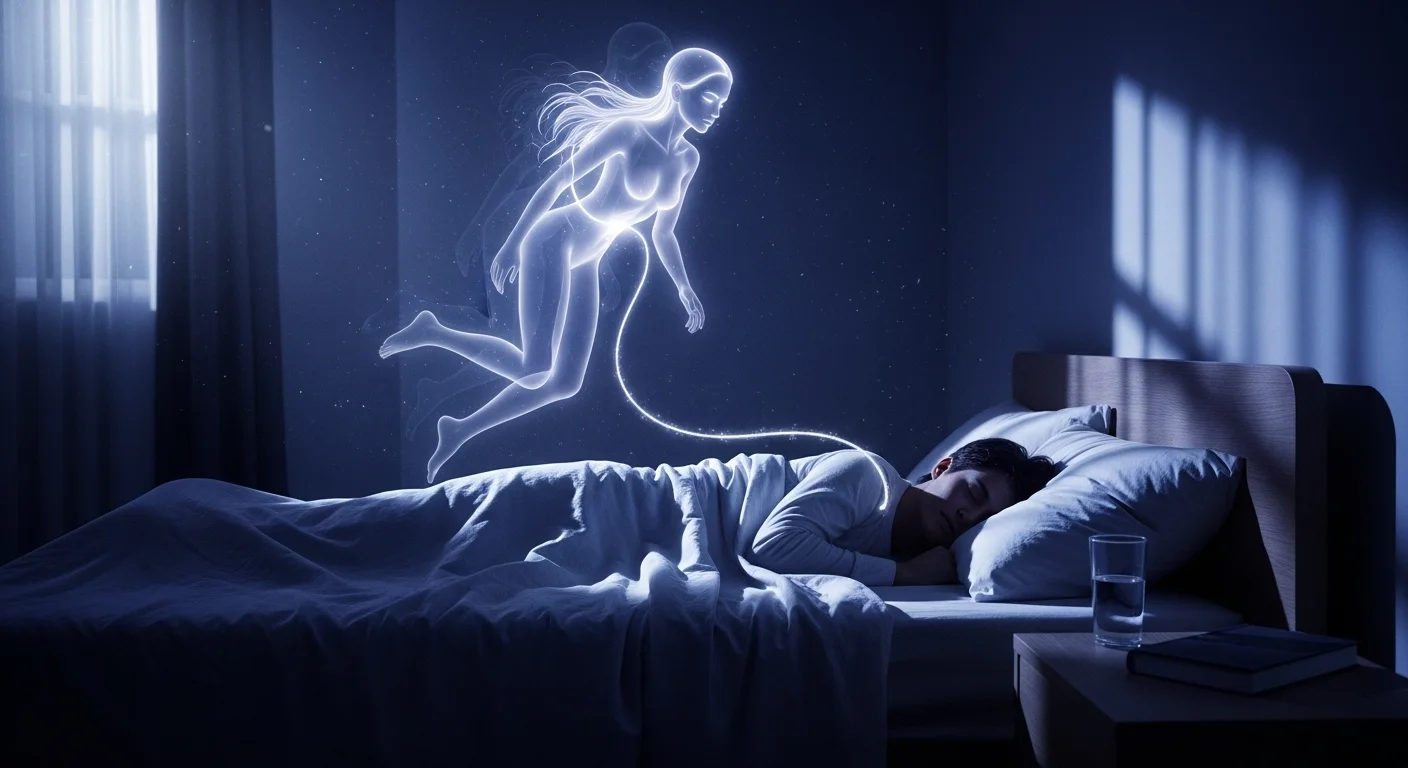
An out-of-body experience occurs when a person feels separated from their physical body. Individuals often report a sensation of floating upwards or hovering near the ceiling. During this event, they may look down and see their own physical form lying on a bed or the ground. This visual perspective is usually clear and distinct from a dream state. The observer often feels weightless and free from any physical pain or restrictions that affect the body below.
The sensory perception during this state differs from normal waking consciousness. Many people describe the ability to see in all directions simultaneously rather than just forward. Hearing remains acute, and individuals often recall specific conversations between medical staff or family members present in the room. Some reports include the ability to move through solid objects like walls or doors. These perceptions occur while the person feels completely detached from the physical processes happening to their biological body.
A sense of extreme calm typically accompanies the visual and auditory sensations. Individuals rarely report feeling fear or panic during the separation phase. Instead, they describe a state of neutrality or peace while observing the scene. This sensation ends when the consciousness returns to the physical body. The reconnection is often sudden and immediate. Once back inside the body, the person resumes normal physical sensation and often feels the return of pain or physical weight.
Common Phases Reported by Survivors
Many survivors describe an initial sensation of separation from their physical bodies. This is frequently called an out-of-body experience. Individuals report floating above the room and observing medical personnel working on them. They often claim to hear specific conversations or see distinct details from this perspective. The feeling during this phase is usually described as painless and peaceful. Reports indicate that the person feels detached from the physical trauma that is occurring below their viewpoint.
The next phase typically involves movement through a dark space or a tunnel structure. Survivors explain that they move rapidly through this darkness toward a bright light. This light is often described as intense but not painful to the eyes. Some individuals report sensing a presence or meeting deceased relatives during this transition. This stage usually brings a sense of comfort and unconditional acceptance. The movement continues until the individual reaches the source of the brilliance.
The final phase involves reaching a limit or a border that represents a point of no return. At this boundary, some people experience a rapid review of their life events and memories. They then realize they must return to their physical bodies to continue their lives. This return is often described as sudden and physically jarring. The individual wakes up in pain or confusion within their body. This specific event marks the conclusion of the near-death experience.

Neuroscientific Explanations for the Phenomenon
Researchers suggest that near-death experiences result from specific chemical changes in the brain. When the heart stops, the brain suffers from a lack of oxygen, a condition known as hypoxia. This state triggers a massive release of neurotransmitters. High levels of glutamate can cause visual hallucinations and a sense of detachment. Simultaneously, the brain releases endorphins to reduce pain and stress. These combined chemical reactions create the intense feelings of peace and euphoria often reported by patients during these critical events.
Scientists have identified the temporoparietal junction as a key area for out-of-body sensations. This region of the brain processes sensory information from the body to create a sense of self-location. Dysfunction in this area disrupts the integration of vision and touch. Studies show that electrical stimulation of this junction can induce the sensation of floating above the body. This evidence indicates that the feeling of leaving the physical form originates from errors in sensory processing within the cerebral cortex.
Another theory involves the intrusion of Rapid Eye Movement sleep into wakefulness. During this state, the brain remains active while the body is paralyzed. This condition can explain visual hallucinations and the inability to move. Additionally, recent studies on dying brains observe a sudden surge of organized electrical activity. This final burst of neural energy may be responsible for the hyper-real memories and the life review phenomenon. These findings provide biological mechanisms for experiences that previously seemed supernatural.
The Role of Oxygen Deprivation in the Brain
Oxygen deprivation, known as cerebral hypoxia, occurs when the brain does not receive enough oxygen to function correctly. This condition often happens during cardiac arrest or severe trauma. When blood flow stops, the brain loses its supply of oxygen and glucose within seconds. This loss triggers a series of chemical changes in the neurons. These changes disrupt normal electrical activity and communication between different parts of the brain. The brain begins to malfunction almost immediately after the supply is cut.
Scientists suggest that this disruption causes specific sensory experiences often reported during near-death events. As the visual cortex loses oxygen, the peripheral vision fails first. This failure creates a sensation of tunnel vision or seeing a bright light in the center of a dark field. Auditory processing may also change, causing buzzing or ringing sounds. These hallucinations result from the random firing of neurons that are struggling to maintain stability without adequate energy resources.
Oxygen deprivation also affects the temporal parietal junction, a brain region responsible for processing sensory data and body image. When this area malfunctions, it may fail to integrate sensory input correctly. This failure can cause the sensation of floating or viewing one’s body from outside. Researchers observe similar effects when they stimulate this brain region electrically during surgery. Therefore, many experts conclude that a lack of oxygen provides a biological explanation for these specific phenomena.
Long-Term Psychological Effects on Individuals
Individuals who survive a near-death experience often report a significant shift in their fundamental outlook on life. A common effect is a greatly reduced fear of death and a stronger belief in an afterlife. Many survivors express a heightened appreciation for existence and small daily details that they previously ignored. This new perspective frequently leads to a reevaluation of personal priorities and values. They tend to focus less on material possessions and more on meaningful relationships.
These psychological shifts usually result in observable behavioral changes over time. Survivors often display increased altruism and a stronger desire to help others. They may become more compassionate and patient in their interactions with family and strangers. Research suggests that these individuals often seek professions or activities that allow them to serve their communities. Consequently, their personal relationships may transform as they adopt a more accepting and less competitive approach to social interactions.
Despite positive changes, some individuals face psychological challenges after the event. The magnitude of the experience can make integration into daily life difficult and stressful. Survivors might feel isolated if they cannot find people who understand what happened to them. Some may experience depression or anxiety as they struggle to reconcile their new perspective with their previous lifestyle. Professional counseling is sometimes necessary to help these individuals process the event and adjust to their new psychological reality.
our next step
If you already understand what astral projection is and you’re looking for practices that truly work, this e-book presents 35 tested techniques to induce out-of-body experiences. Each technique is explained clearly and directly, allowing you to choose the method that best fits your routine and level of awareness.
This material is ideal for those who want to apply objective and varied methods, speeding up the process of conscious out-of-body projection. It works for both beginners and practitioners who have already had experiences and want to expand their possibilities. This is a practical guide for anyone who wants consistent results.

If you are taking your first steps and want to understand the fundamentals of astral projection with clarity, this manual was created to make your learning easier. In it, you will find clear explanations about the subtle bodies, the stages of projection, the most common sensations, and how to deal with fear and mental blocks.
This e-book is recommended for anyone who needs a solid and safe foundation to start practicing with confidence. It organizes the concepts in a progressive way, helping you understand the process as a whole and develop a consistent and conscious practice.

For those who want more complete and in-depth guidance, the complete astral projection course offers structured lessons, guided practices, visualizations, advanced techniques, and ongoing support. The content was designed to take you from theory to practice with safety and consistency.
This course is suitable for all levels, from beginner to advanced, and provides a systematic approach based on years of research, experience, and proven results. You will learn how to awaken your potential, gain control of your experiences, and integrate spiritual insights into your daily life.